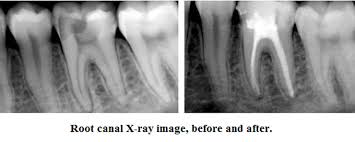
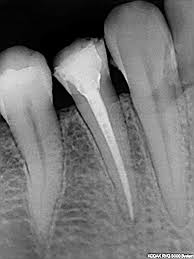
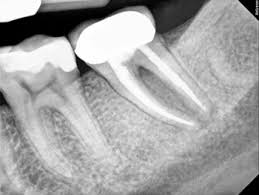
Root Canal Treatment
Root canal is a treatment to repair and save a badly damaged or infected tooth instead of removing it. The term "root canal" comes from cleaning of the canals inside a tooth's root. Decades ago, root canal treatments often were painful.With dental advances and local anesthetics, most people have little if any pain with a root canal. In fact, it's probably more painful living with a decayed tooth. Root canal alternatives include extracting the damaged tooth and replacing it with a dental implant, bridge or removable partial denture.
To understand a root canal procedure, it helps to know about the anatomy of the tooth. Inside the tooth, under the white enamel and a hard layer called the dentin, is a soft tissue called the pulp. The pulp contains blood vessels, nerves and connective tissue, and helps to grow the root of your tooth during development. In a fully developed tooth, the tooth can survive without the pulp because the tooth continues to be nourished by the tissues surrounding it.
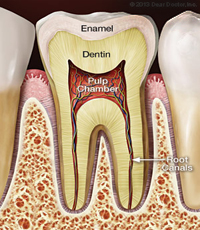
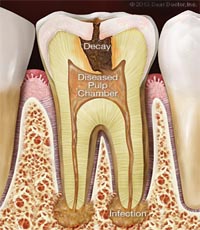
The pulp is the living tissue of the tooth with blood supply and nerve supply. Once the dental caries (decay) involves the pulp, the pulp gets infected causing pain. The aim of the root canal treatment is to remove the infected pulp. This is done by removing the infected pulp with files in the pulp chamber and cleaning and shaping the root canals and sealing the canal with a filling material.
CROWN : This is the part of the tooth you can see above the gumline. ROOT : This part of the tooth sits in the bone below the gum. The root of your tooth is usually twice as long as the crown, the part you see above the gumline.
The Story Of Root Canal Therapy
Each tooth has a soft tissue – the pulp which nourishes the tooth. Because of deep decay, injury, or gum disease, the pulp tissue in your tooth has become inflamed or infected. In any other part of your body, if a similar tissue becomes diseased, the body merely throws it off and forms new tissue. However, a tooth is a unique and different. Because the infected soft tissue (pulp) within the tooth is totally encased within hard tissue, it is the role of the dentist to remove the soft tissue located in the root canals, cleanse the area, and finally fill the canals with a special material so that bacteria cannot re-enter the tooth to cause another infection. When the endodontic treatment is complete, the tooth is by no means "dead". It receives quite adequate support from the surrounding tissues and may be expected to last as long as any other natural tooth.
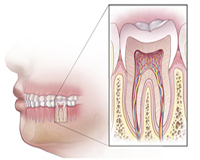
Step 1 Getting started on root canal treatment
A root canal is usually done by an endodontist or a general dentist. The root canal usually takes one or two visits, but once in a while additional visits are required because some teeth prove difficult to treat.
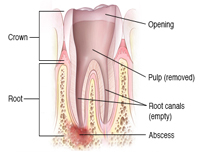
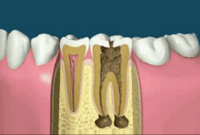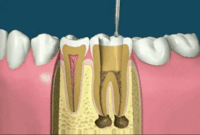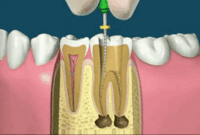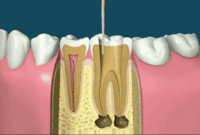
Step 2 Clearing up root canal infection
After the diseased pulp is removed, the pulp chamber and root canals are flushed and cleaned
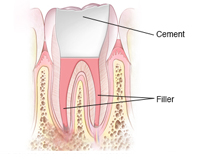
Step 3 Filling the root canals
After cleaning and drying, it's time to fill the interior of the tooth the empty pulp chamber and root canals.
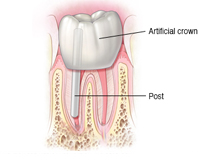
Step 4 Final stage of a root canal
The final stage of the root canal is restoring your tooth. Because the tooth typically has a large filling or is weakened from extensive decay, it needs to be protected from future damage and returned to normal function.
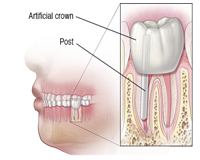
Step 5 After your root canal
After your root canal, your restored tooth with the new crown should work normally and look cosmetically pleasing.
We use Apex Locater and Endo Motor for Advance Root Canal Treatment
Apex Locater
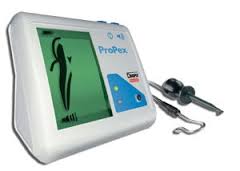
This equipment helps make Root Canal Treatment more accurate, predictable and less time consuming. Also helps eliminate the use of multiple unnecessary X-rays during Root Canal Treatment (RCT).ProPex Apex Locator is the good device that gives Improved visualization of the file progression with the large colour screen,Progressive sound control enabling additional control of the file progression.
Endo Motor
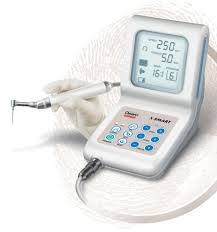
Endo Motor used for General Dental Practitioners performing root canal treatments with the reciprocating, single file technique or traditional continuous rotation file systems. It enables the practitioner to fully focus on the patient and the treatment due to its simplicity of use, as well as the excellent visibility and access with the miniature contra-angle attachment.
Actual Root Canal Treatment