Pediatric Dentistry

Pediatric Dentistry is a dental specialty that concentrates its attention on infants and children providing preventive and therapeutic oral health care. During the "growth" phase of a child, special approaches are needed to guide the dental growth and development in order to avoid future dental problems.
A common question that parents ask is "why spend on the maintenance of milk teeth when they are to be finally replaced by the permanent ones?"
Milk teeth are as important as the permanent ones because- Baby teeth are important in proper feeding and nutrition.
- Milk teeth serve as space maintainers for the proper spacing and alignment of the permanent teeth.
- Healthy milk teeth are crucial in helping the baby learn how to speak properly.
- Healthy looking teeth are important in building self-confidence at an early age. Small children because of immaturity are quick to tease peers about ugly looking or decayed teeth.
First Visit
First checkup before your child turns one. The purpose of this visit is for a preventive exam only. Your child's clean, healthy teeth are important in so many ways. The earlier the first dental visit will be the better will be the chances of preventing any further dental problems. During first visit,
- Examination and diagnosis check for tooth decay or other dental problems.
- Scaling and polishing of teeth, fluoride application and sealant for prevention of caries.
- Advise the parents about the child's dental hygiene and problems like thumbsucking, mouth breathing, tongue thrusting and nursing bottle decay.
- Identify your child's fluoride needs.
- Get the child used with the dental office environment and the dentist.
Treatments
- Pit and Fissure sealants :
- Root Canal Treatment in milk teeth :
- Space Maintainers :
- Fluoride application :
The chewing surfaces of teeth are never flat. They have in fact certain depressions called Pit and Fissures which serve as potential traps for food and bacteria making the teeth susceptible for decay. Although other factors such as dietary habits, oral hygiene and amount of sugar intake also pays important role, but the pits and fissures have been suggested as the single most important anatomic feature leading to the development of tooth decay. Therefore as a preventive measure we fill certain deep pits and fissures we see with dental sealants so as to prevent dental caries in deciduous teeth.
In cases where tooth decay extends deep into the nerve portion of the tooth it might be necessary to perform a root canal as described for the permanent tooth. Although the morphology of milk teeth makes the treatment difficult, it might still be considered as a better alternative to tooth extraction.
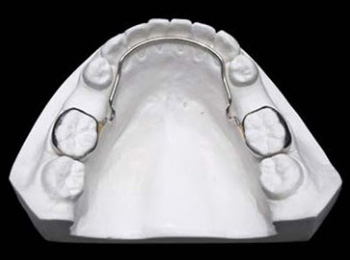
A space maintainer is a removable or fixed appliance designed to maintain an existing space. Space maintainers are usually fitted in children when they have lost baby teeth early. The gap left from losing this tooth needs to be held open for the permanent tooth to erupt in the correct position.
A child's teeth are more prone to decay due to lack of proper dexterity of brushing. Application of fluoride varnishes at regular intervals strengthens the tooth structure by incorporating fluoride ions into the structure making them more prone to acid dissolution. Not only do the permanent but also milk teeth benefit from fluoride treatment.
Dental Conditions to be taken care of -
- Baby Bottle Tooth Decay (Nursing Bottle Caries):
- Oral habits in children:
The term describes a dental condition which involves the rapid decay of many or all the baby teeth of an infant or child. The teeth most likely to be damaged are the upper front teeth since they are the first teeth to erupt and thus have the longest exposure time to the sugars in the feeding bottle. The lower front teeth tend to be protected by the tongue as the child sucks on the nipple of the bottle or the breast.
Baby Bottle Tooth Decay is caused by long exposure of a child's teeth to liquid containing sugars generally when the baby falls asleep with a bottle containing milk or juice or a pacifier dipped in honey. The liquid pools around the front teeth. During sleep, the bacteria living in every baby's mouth, turns the milk sugar or other sugars to acid which causes the decay.
By the time the condition is noticed by the parents it may be too late and extractions of the decayed teeth may be necessary. As a result, your child may suffer from long term disorders which include speech impediments, possible psychological damage, crooked or crowded teeth, and poor oral health.
The condition can be easily prevented by -1. Clean your child's teeth daily 2. Giving plain water after a bottle of juice, milk, or formula 3. Start bottle weaning by at least a year 4. Make sure your child gets the fluoride needed to prevent decay 5. Have regular dental visits for your child beginning when their first tooth erupts
Frequently children acquire certain habits that may either temporarily or permanently be harmful to teeth and tooth supporting structures. These habits are acquired as a result of repetition. In the initial stages there is a conscious effort to perform the act. Later the act becomes less conscious and if repeated often enough may enter the realms of unconsciousness.
Some common oral habits seen in children include thumb sucking, mouth breathing, tongue thrusting, lip biting, grinding of teeth and nail biting.
